Gas Exhange
Pulse Oximetry
While the ability to perform pulse oximetry has been available for the past 30 years, it is only in the past 10 years that the cost of the technology has dropped to the point where it is accessible for the general population. A recent search on Amazon, revealed consumer grade pulse oximeters for $20. It is so prevalent a technology that it is built into almost all smart phones, watches and helath monitoring devices (i.e. Fitbits). Every outpatient practice I have been affilaited with appropriately considers SaO2 a routine part of the vital signs
All pulse oximeters on the market today rely on the diffential absorption of oxygenation and deoxygenation blood in the red and near infra-red region. In addition during the course of a cardiac cycle the amount of blood in the venous system is relatively static while the arterial blood volume changes with each systolic ejection. By measuring the changes in light absorption during the cardiac cycle, the pulse oximeter is able to isolate the arterial blood component and calculate the saturation of hemoglobin with oxygen (SaO2).
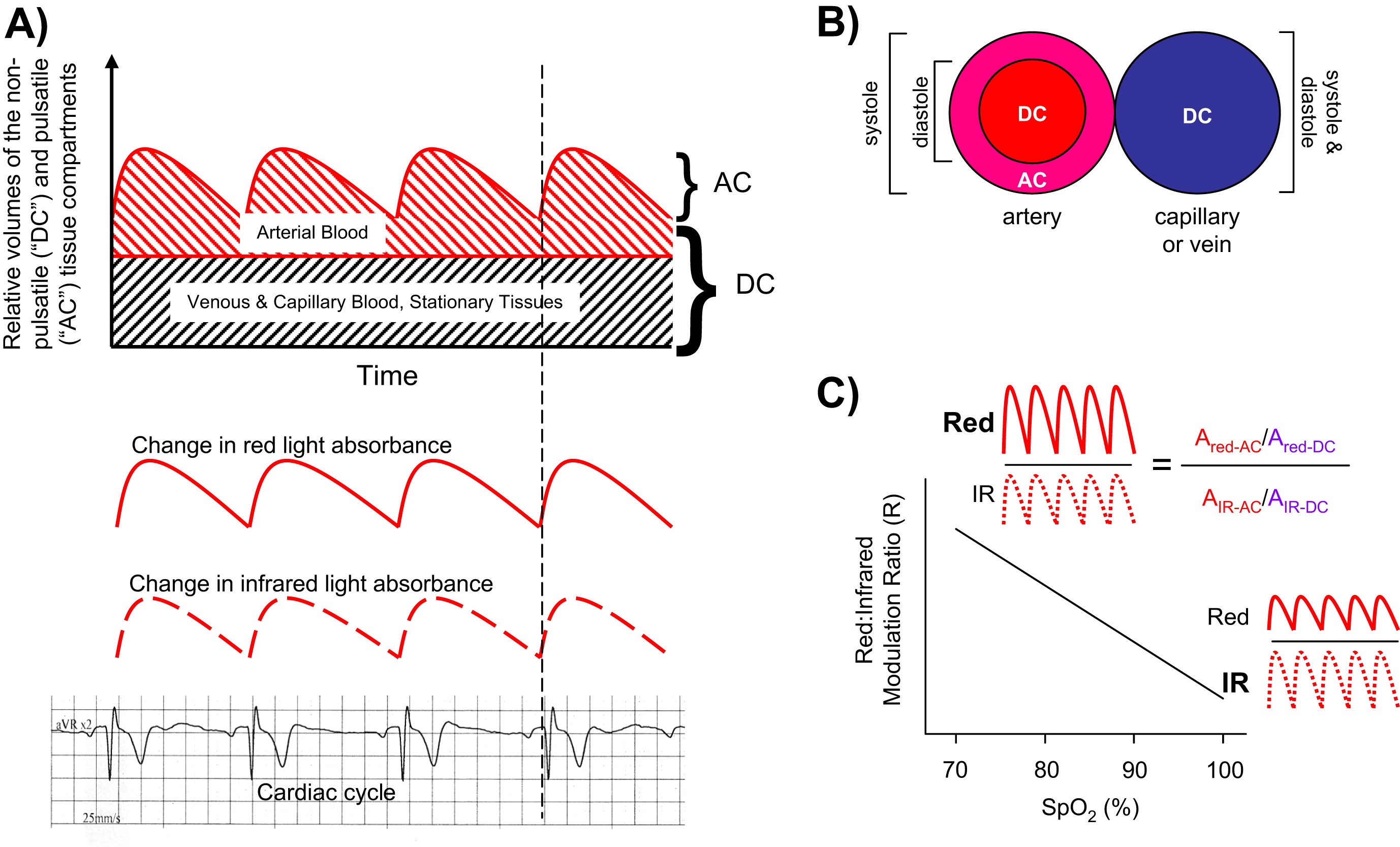
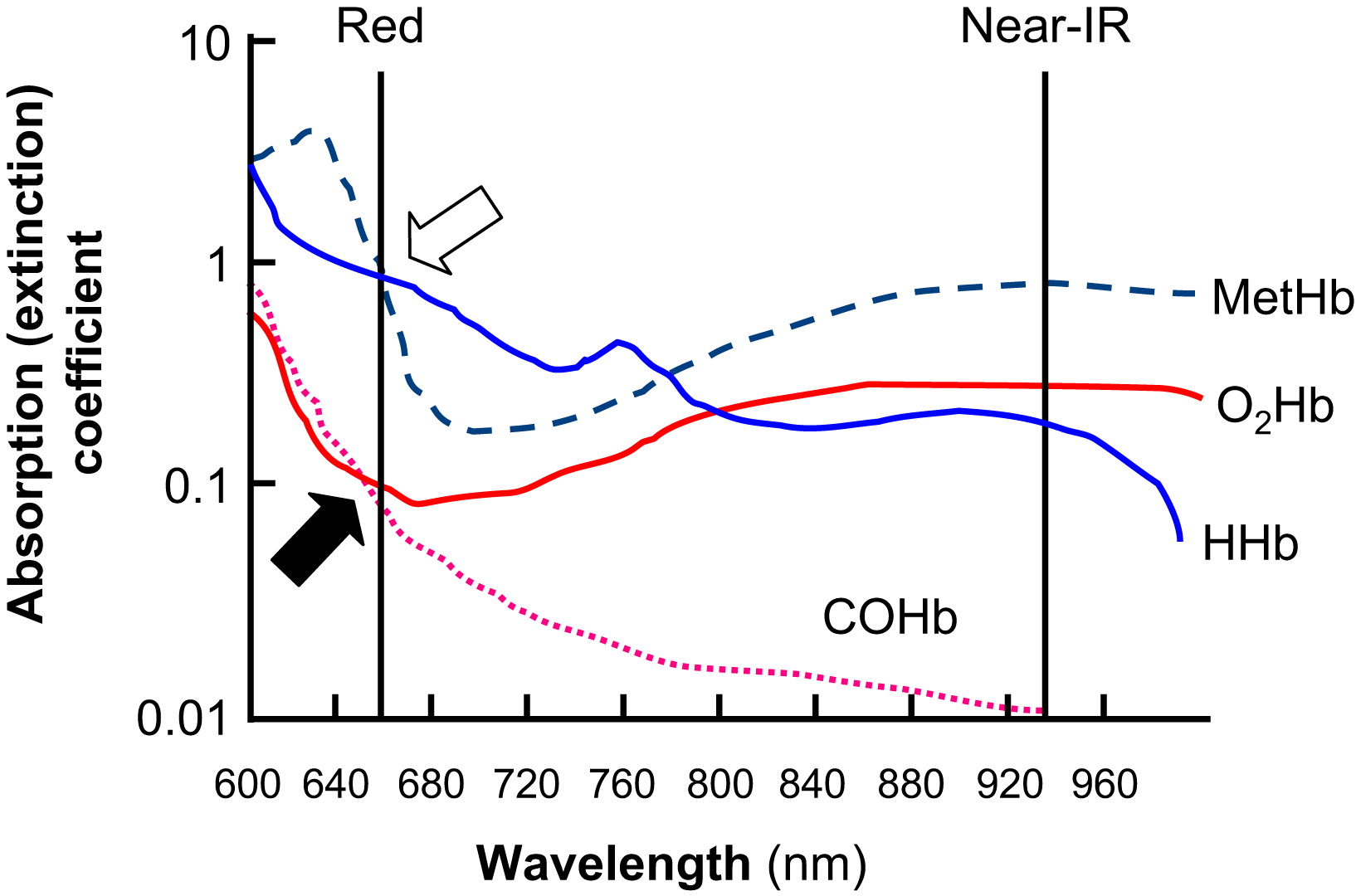
Having spent several decades in medical practice I have witnessed medical equipment evolve. One day many years ago we were clearing out a store room and came across an early pulse oximeter that was used in the clinic. The device required wall current, weight several pounds, and most likely had cost several hundreds of dollars when new. Now battery powered fingertip devices are the norm. Concern has been raised on the heels of the COVID epidemic about the accuracy of consumer grade pulse oximeters. There was a recent incident where a patient demanded an appointment because of her poor saturations at home. There was no function change in her respiratory capacity and when we checked her SaO2 in the office it was normal. She thankfully has brought into the office her device from home that she purchanced from a foreign website that promises to let 'you shop like a billionaire'. The device was giving eronous information and was not worth the $7 she paid for it. Desppite the example, there has been limited studies that have tested non-FDA approved devices and found many to be reasonably accurate.
What physical factors can influence the ability and accuracy of pulse oximetry measurement?
What poisoning exposures can impact the accuracy of pulse oximetry readings?
\A potential limitation of pulse oximetry is that we are measuring hemoglobin saturation, which is closely related but not synonomous with the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood stream. In 1904, a Danish physiologist, Christain Bohr, discovered a relationship between hemoglobin saturation and both metabolic and respiratory disturbances that bears his name.
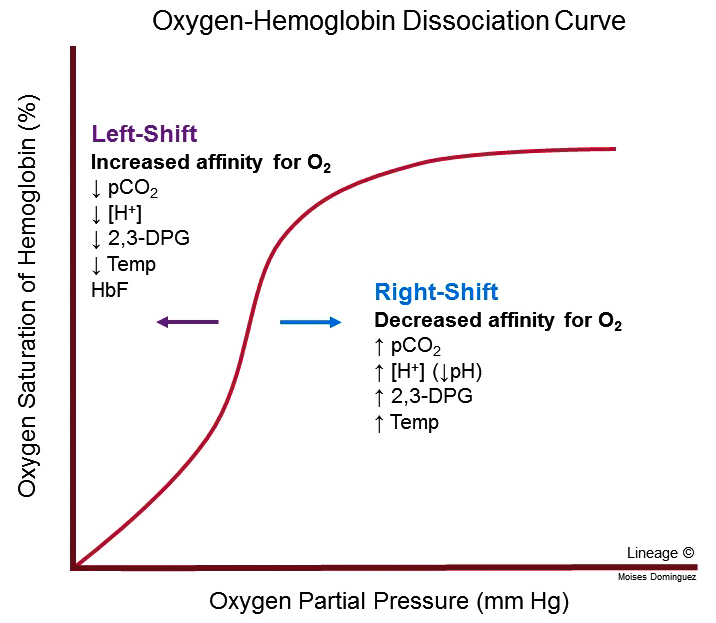
How does a developing fetus take advantage of this relationship?
In what pathophysiologic situations does the Bohr Effect facilitate oxygen delivery to tissues?
What is a common scenario where a patient may have an "adequate" SaO2 but in fact be hypoxemic?
Exercise Pulse Oximetry
Under conditions of health, the saturation of the hemoglobin molecule in the pulmonary circulation is extremely efficient. As we increase cardiac output with physical activity, primarily by increasing heart rate, the time the red cell spends in the pulmonary circulation begin to diminish. Even at VO2max, the red cell in in the pulmonary circulation for 0.25sec. The implication is that under circumstances of health, even maximal physical exertion will not result in desaturation.
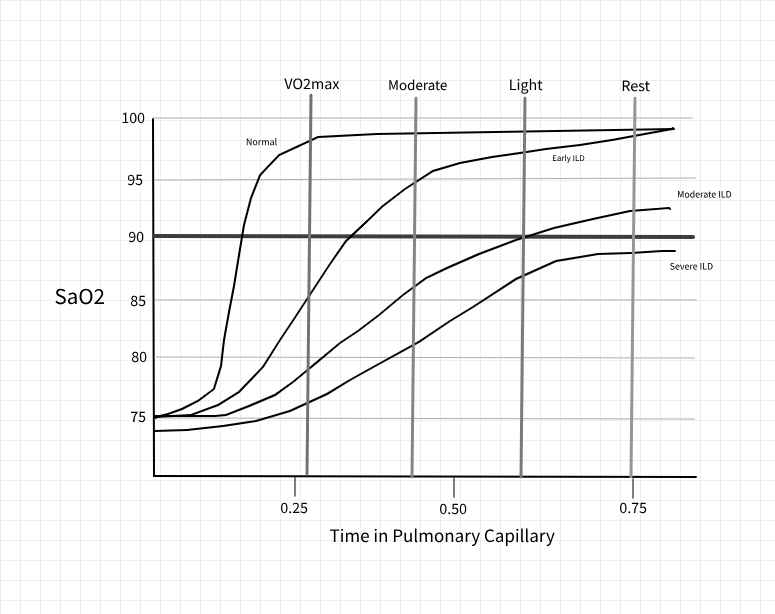
In situations where there is impairment in the interstitial surface, the time for the red cell to become completely saturated lengthens. Eventually is will reach the point where even at rest the red cell will leave the pulmonary circulation and not be completely saturated. This is an indicator of fairly advanced disease.
For patient's with earlier disease, exercise oximetry can be a high yield diagnostic procedure. In this situation there is adequate time at rest for normal arterial oxygen saturation. As heart rate increases and the time in the pulmonary circulation diminishes, even mild levels of exertion will result in abnormal SaO2 levels.
In addition to the diagnostic value, this is also accepted as an indicator for the prescription of supplemental oxygen. One practical caveat to simple exercise testing in the office environment, it that there is a lag between the oxygenation of a red blood cell in the lungs and that same cell making it to the finger tip where your pulse oximeter is located.
I encourage my staff to continue to measure SaO2 for at least 2 minutes after the patient stops physical activity due to dyspnea, for you may not see the desaturation until the recovery period.
What physiologic processes can aggravate the drop SaO2 levels in patient's with exercise desaturation?
Overnight Pulse Oximetry
Respiratory physiology may be quite different at night and may be the sole area where a patient experiences clinically important desaturation. A common response when I discuss nocturnal desaturation given the high prevalence of pulse oximeters is "whenever I wake up and check my oxygen level it is just fine". Given the fact that we must be awake for three minutes for our brain to process an experience as a memory, the time it would take to sleep inertia to allow a person to find and turn on a pulse oximeter, and the 1+min delay for a consumer grade pulse oximeter to record a value, spot checks for SaO2 have no correlation with the duration or severity of sleep related desaturation.
An overnight oximeter records the SaO2 value every few seconds and internally records that data. While devices that have this capability are available at a consumer level their cost to 5-10 times higher than a device that performs spot checks.
In addition when this information is being used for determination of oxygen need, it must be performed by a "neutral" party.
VitruOx has a business model based on the independent performance of overnight pulse oximetry. Below is a sample of an overnight oximetry report.
What conditions should one consider in evaluating desaturation on overnight pulse oximetry?
What is the limitation of pulse oximetry in assessing these conditions?
Six Minute Walk
Simple exercise oximetry has no parameters for the intensity or duration of physical activity. The 6-minute walk, however, does incorporate some additional measurement parameters as well as instructions to the patient which significantly increases the diagnostic yield of this procedure.
With a 6-minute walk the patient is placed on a level surface and given instructions to walk at a pace of their choosing. During the 6-minute timeframe the patient may stop and rest for as long as they feel is necessary.
The parameters measured during the study include the patient's pulse rate and saturation levels every minute as well as the total distance covered over the course of 6 minutes.
In addition to the information that can be gleaned with regards to the presence of exercise desaturation there are also prediction equations based on gender, height, age, and weight.
Male predicted in meters = (7.57 * height in cm) - (5.02 * age) - (1.76 * weight in kg) -309
Female predicted in meters = (2.11* height in cm) - (2.29 * weight in kg) - (5.78 * age) + 667
when performed as a serial measurement, a 45m change is considered clinically significant.
The test has been used in numerous conditions including:
- arthritis
- fibromyalgia
- geriatrics
- multiple sclerosis
- parkinson's disease
- COPD
- Interstitial Lung Disease
- lung transplant assessment
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- and others....
In pulmonary conditions it has been shown to have a better predictive value for mortality than pulmonary functions studies.
What are we measuring with a 6 minute walk that we may fail to capture in resting oximetry or PFTs?