Gas Exhange
Exercise Pulse Oximetry
Under conditions of health, the saturation of the hemoglobin molecule in the pulmonary circulation is extremely efficient. As we increase cardiac output with physical activity, primarily by increasing heart rate, the time the red cell spends in the pulmonary circulation begin to diminish. Even at VO2max, the red cell in in the pulmonary circulation for 0.25sec. The implication is that under circumstances of health, even maximal physical exertion will not result in desaturation.
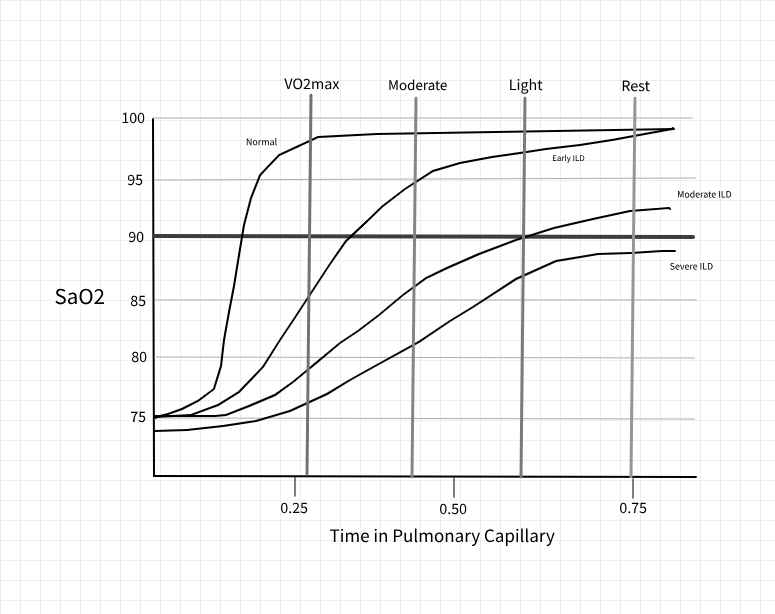
In situations where there is impairment in the interstitial surface, the time for the red cell to become completely saturated lengthens. Eventually is will reach the point where even at rest the red cell will leave the pulmonary circulation and not be completely saturated. This is an indicator of fairly advanced disease.
For patient's with earlier disease, exercise oximetry can be a high yield diagnostic procedure. In this situation there is adequate time at rest for normal arterial oxygen saturation. As heart rate increases and the time in the pulmonary circulation diminishes, even mild levels of exertion will result in abnormal SaO2 levels.
In addition to the diagnostic value, this is also accepted as an indicator for the prescription of supplemental oxygen. One practical caveat to simple exercise testing in the office environment, it that there is a lag between the oxygenation of a red blood cell in the lungs and that same cell making it to the finger tip where your pulse oximeter is located.
I encourage my staff to continue to measure SaO2 for at least 2 minutes after the patient stops physical activity due to dyspnea, for you may not see the desaturation until the recovery period.